Application notes
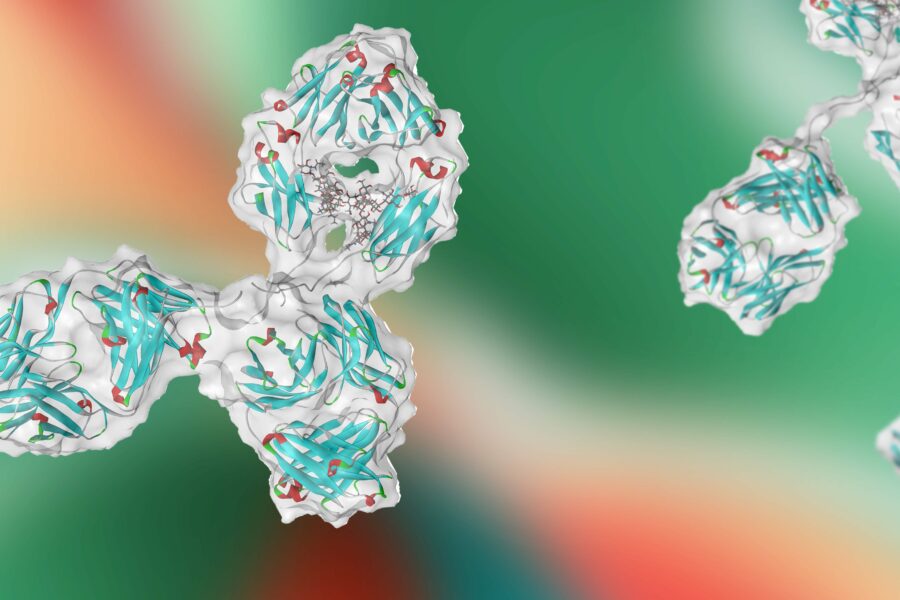
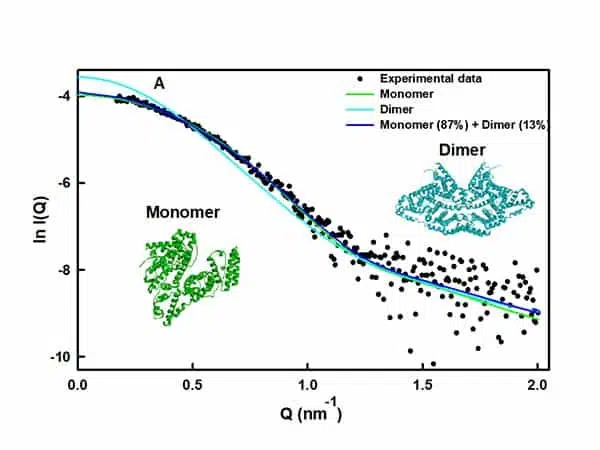
Probing Antibody conformation and interactions with SAXS: Effects of Concentration and Salt
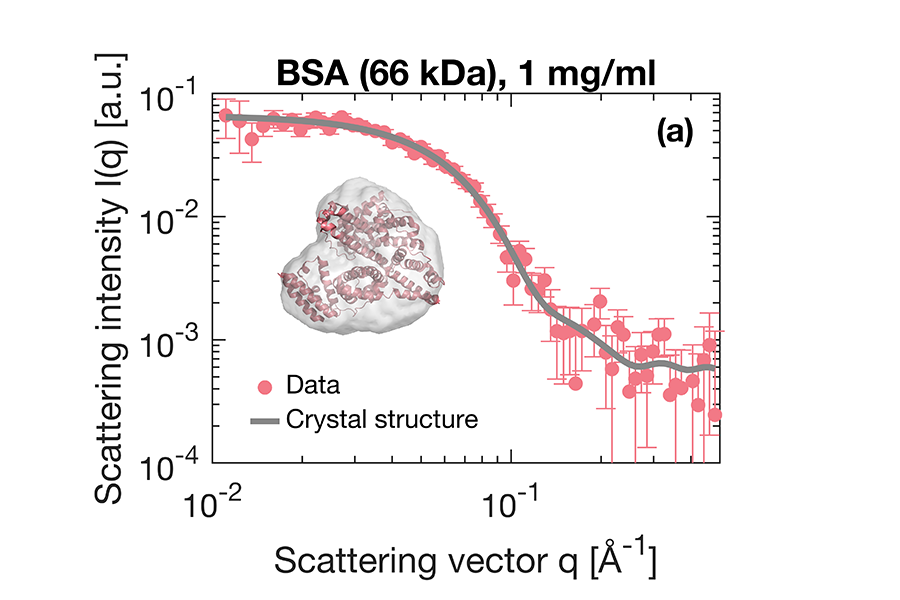
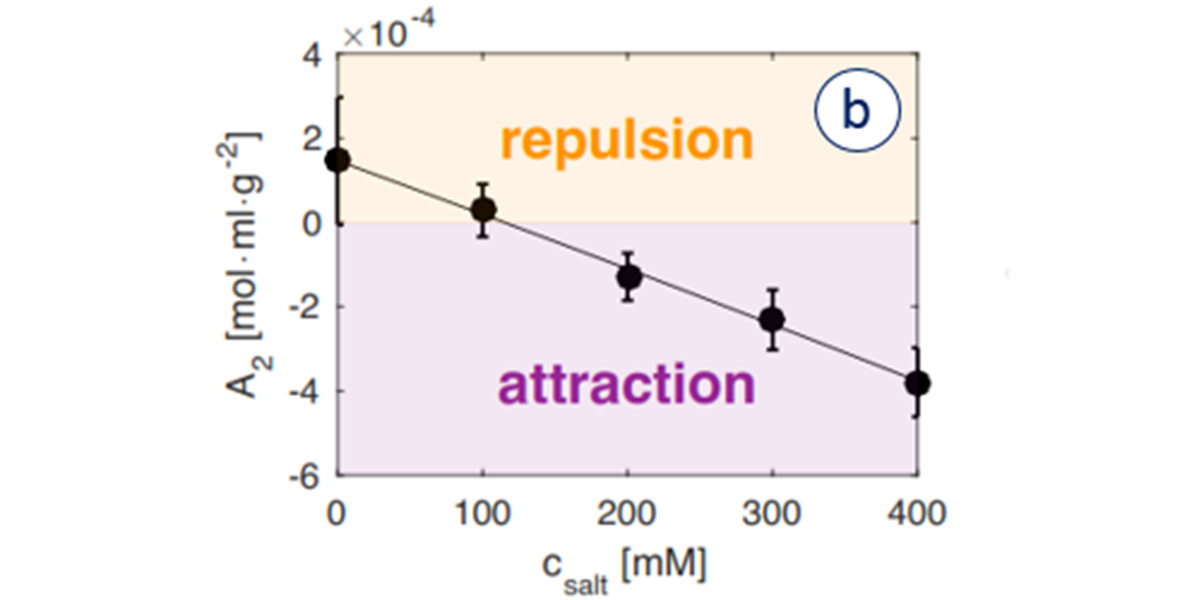
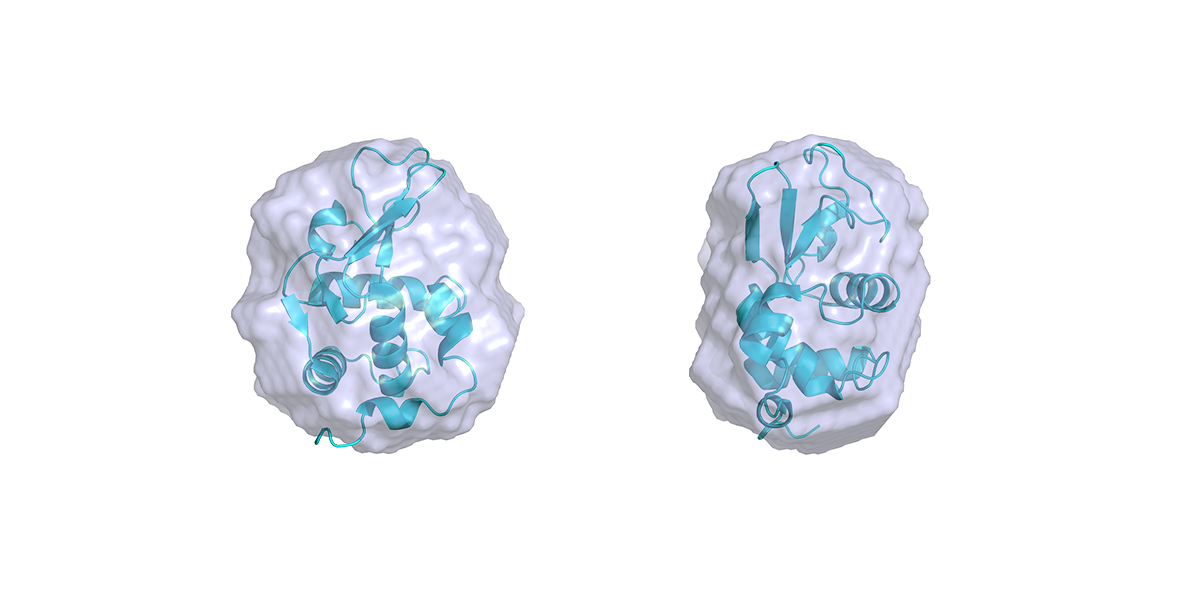
Biotherapeutics, particularly monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), are well-established therapies recognized for their...
SAXS: an efficient tool for studying the size and structure of small peptides
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) is a versatile technique for analyzing small peptides in solution, offering detailed insights into their size, structure, and self-assembly.
Laboratory SEC-SAXS: a comprehensive approach to biological sample analysis
The structural and conformational stability of biological samples presents significant challenges due to...
Lamellae structure and crystallinity analysis of semicrystalline polymers
Polyvinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene (PVDF-TrFE) is a versatile piezoelectric polymer well-known and studied for its ferroelectric and pyroelectric properties.
Size distribution of Gold Nanoparticles
SAXS was employed to characterize various complex nanoparticle samples: monodisperse systems (with a narrow standard deviation or broad distribution) and bimodal mixtures with different ratios. Nanoparticles (NPs) are indispensable in numerous applications, ranging from coatings and cosmetics to drug delivery systems, where they are frequently employed even at exceptionally low…
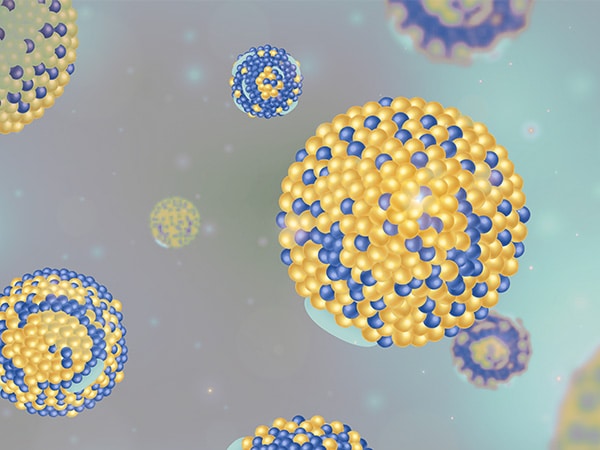
Phase diagram of lipid nanoparticles obtained with SAXS
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) have attracted considerable attention as promising drug carriers due to their biocompatibility and ability to encapsulate...
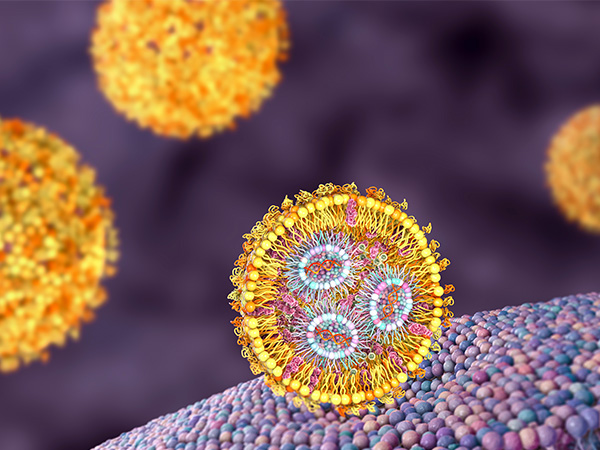
SAXS as a tool to study Lipid Nanoparticles
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are one of the most exciting technologies in the drug delivery world. Previously used to study lipid nanoparticles and lipoplexes, small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) has proven to be an excellent technique for characterizing the structure of LNPs.
Cellulose nanocrystals under shear studied by SAXS
The structural evolution of cellulose nanocrystals under shear is monitored using two different SAXS set-ups In the last two decades, bio-based nanomaterials have attracted increasing research interest for applications in a multitude of industrial sectors. Moreover, with soaring oil prices and the rising consumer appeal toward sustainable products, market growth…
Shear alignment of Pluronic block copolymers
The structural evolution of P123 Pluronics was monitored and analyzed through shearSAXS measurements performed with the Xenocs Couette stage Poloxamers, also known under commercial names as Pluronics®, Synperonics® or Kolliphor® are a class of synthetic triblock copolymers that are composed of polyethylene oxide (PEO) and polypropylene oxide (PPO) blocks. They…
Shearing of clay minerals in suspension
Investigation of smectite suspension shear behavior through SAXS measurements performed with the Xenocs Couette stage Clay minerals are a group of hydrous aluminosilicate minerals that are commonly found in soils, sediments, and rocks. The most common types include kaolinite, illite, and smectite, each with its own distinct characteristics and uses.…
Mass specific surface area determined by SAXS
In this Application Note, the XSACT software package is used to process the SAXS data and determine the specific surface area of SiO2 powder samples. Both the invariant and the absolute-scale methods are employed, and the results are compared with the obtained from BET measurements and analysis.
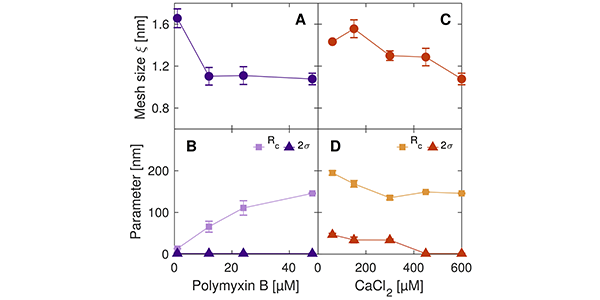
Characterization of protein intermolecular interactions
SAXS was used to study the effect of pH and protein concentration on the self-interaction process of a BSA system in solution Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is a non-glycosylated globular protein found in bovines. It is widely used in drug delivery, immunodiagnostic procedures and in clinical chemistry due to its…
Focused beam for residual stress and texture analysis
Residual stress analysis and texture measurements obtained on thin film samples with the interchangeable auxiliary source (AuX source) of the Xeuss 3.0.
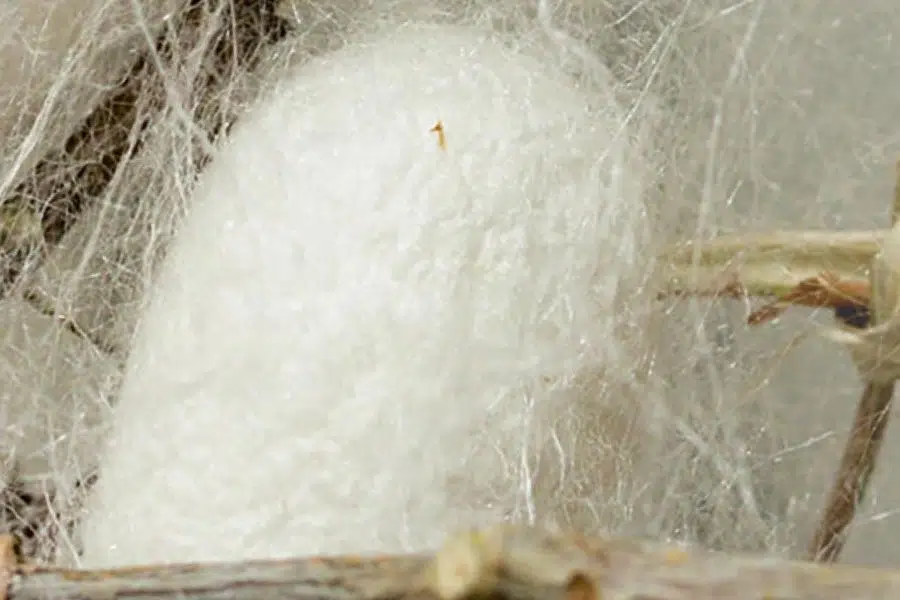
Measurements and analysis of extremely thin single protein fibers
Silks are well known natural protein fibers, spun by spiders, silkworms and other insects, that have been used for centuries in the textile industry due to...
Characterization of protein self-association
Bovine serum albumin (BSA) is a non-glycosylated globular protein found in bovines. It is widely used in drug delivery, immunodiagnostic procedures and in clinical chemistry due to its low cost and...
Fast thermal studies of cocoa butter
Cocoa butter is a highly polymorphic compound exhibiting up to six crystalline forms of glycerides (fatty acids), each defined by different stability and melting point. In order to...
Batch data analysis of particle size temporal evolution studied with SAXS
Time-resolved Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) mesurements, performed during synthesis procedures or other chemical or physical reactions, have the potential to reveal valuable information which can...
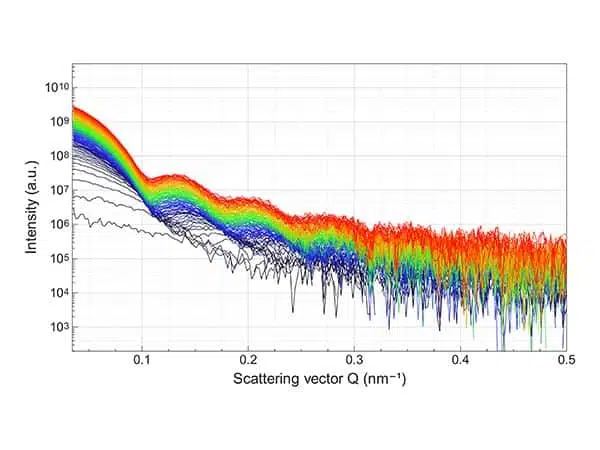
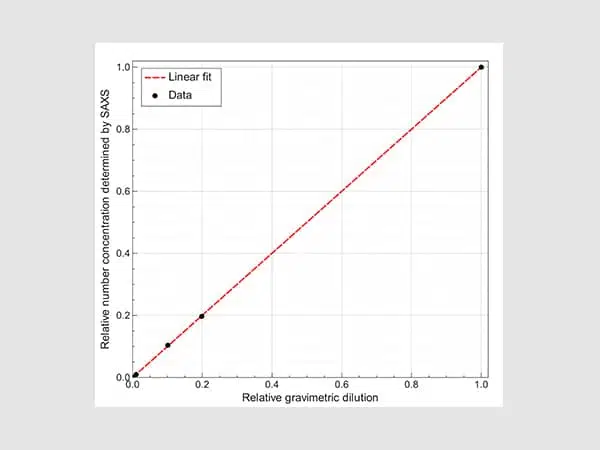
Number concentrations for Gold Nanoparticles: robust and traceable measurements in the lab
SAXS laboratory instruments provide traceable number concentration measurements for nanoparticles. Nanoparticles (NPs) are an essential building block for ...
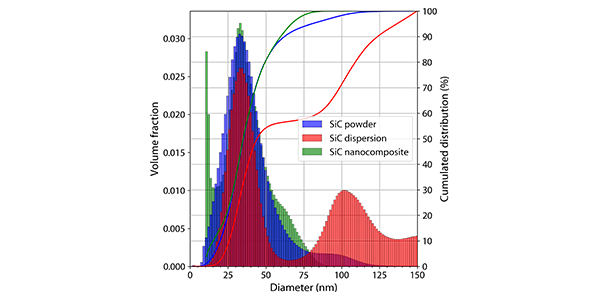
Size distribution of nanoparticles: powders, dispersions and composites
Size distributions of industrial nanoparticles have been determined in various forms for quality assessment and process monitoring. Nanoparticles are being produced at an increasing rate and have become an essential building block for the development of new materials with improved properties. The performance of the final products depends not only…
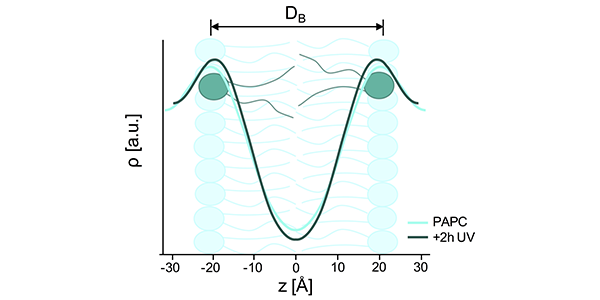
Vesicles
Probing the effect of oxidation on model lipid bilayers The vital function of cells depends strongly on cell membranes which enclose cellular compartments and separate the cell interior from the extracellular domain. Oxidative stress for example damages the cell membrane and is at the origin of many pathological conditions such…
Microgels
Screening of stimuli-responsive colloidal particles Microgels are colloidal particles consisting of cross-linked 3-dimensional polymer networks. These particles have the ability to shrink or swell substantially in response to external stimuli such as temperature, pH, ionic strength and light, allowing triggered release of encapsulated bioactive molecules. They additionally protect these loaded…
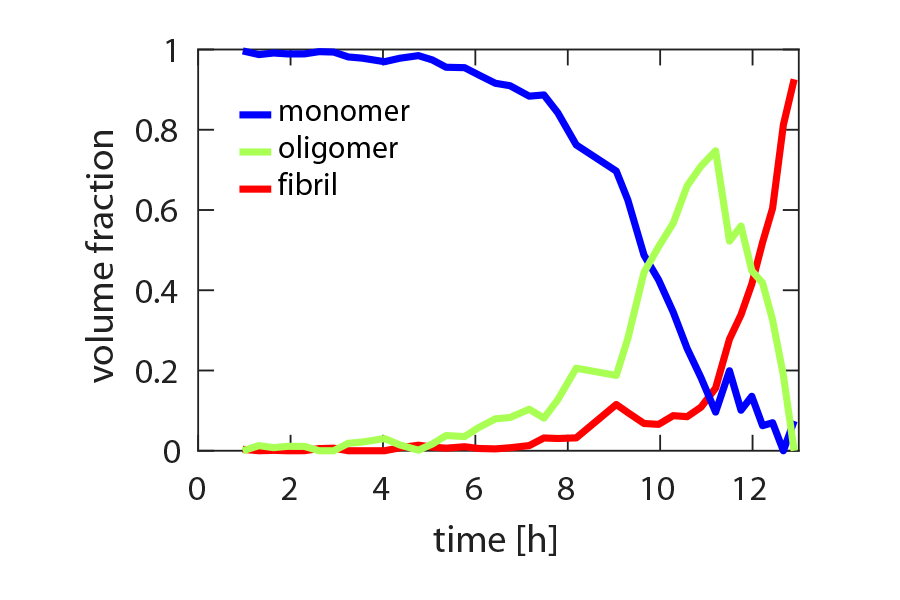
Thorough investigation of oligomers during protein fibrillation
The transient nature of aggregates during the fibrillation process of α-synuclein is highlighted with in-house SAXS experiments using the BioXolver. Protein aggregation into fibrillar structures is associated with a variety of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. It is becoming increasingly evident that the toxic species causing the…
In-lab SEC-SAXS for structural investigation of complex samples
How to study the structure of complex biological samples? High quality data and 3D envelopes can be obtained on small and large proteins with SEC-SAXS in the lab Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is commonly used to investigate the solution structure of biological macromolecules. Highly accurate results can be obtained with…
Protein-protein interactions – from in vivo functionality to pharmaceutics and food science
Salt concentration and pH impact were studied on lysozyme and BSA systems respectively by investigating various parameters (osmotic second virial coefficient, folding state and 3D shape). Protein-protein interactions are relevant for various biological processes, such as transcription and signal transduction, but also for protein crystallization, stability and shelf-life of pharmaceutical…
High throughput protein envelope determination
3D envelopes were determined from an automated sequence of measurements including 3 different proteins with low volume and dilute solutions. Small-angle X-ray scattering is complementary to other structural biology techniques. It provides reliable information on the shape of proteins in solution and associated parameters including macromolecule interactions and dynamics. Reliability of the…
SAXS measurements of diluted solutions
SAXS investigations of Lysozyme solutions were performed enabling the calculation of the radius of gyration (Rg) and of the Pair-distance Distribution Function (PDDF). Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) has become an established technique for studying biological systems and more specifically protein solutions. SAXS is able to characterize both ordered and…
Polymer phase transformation
Simultaneous SAXS/WAXS measurements of a semi-crystalline polymer during thermal processing enables determination of route for phase transformation. It is well known that polymers undergo a large series of thermal transformations, from the synthesis in the reactor up to the final product shaping, i.e. during injection molding processing or film formation.…
Overview of a surfactant structure
SAXS/WAXS measurements were performed on the Head & Shoulders Classic Clean Shampoo from Procter & Gamble and reveal its inner structure. Many personal care products are concentrated surfactant systems displaying a multi-phasic microstructure. To design new properties through innovative formulation and to control the latter during the production process, good…
Investigation of Gold Nanoparticles
Shape and size of gold nanoparticles (NPs) in suspension have been determined by SAXS measurement. NPs are used even at very low concentration in many applications such as coatings, cosmetics or drug delivery.
Silk fiber nanostructure investigation
SAXS/WAXS measurements enable the determination of the characteristic dimensions and the semi-crystalline structure of Bombyx mori cocoon silk fibers. The excellent mechanical properties of silk fibers, such as their high strength and toughness, made them of great practical interest for numerous applications. The most ubiquitous domesticated silkworm, the Bombyx mori,…