Temperature influence on structure
Temperature influence on structure,
what is measured?
The measurement identifies the nanostructure changes with temperature variations.
Temperature range accessible from SAXS Xenocs measurement:
- -150°C to 1000°C with the Nano-inXider and the Xeuss
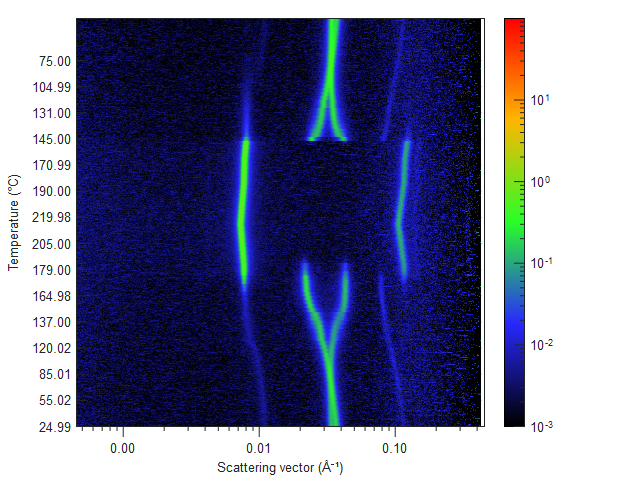
Figure 1. Hysteresis effect in the temperature cycle : data acquired on dithienocyclopenta-thieno-[3,2-b]thiophene (DTCTT)-based molecular donor material for small molecular organic photovoltaic (sm-OPV) devices.
See more details in Y. Abe et al., Chem. Mater., 2017, 29 (18), pp 7686–7696
Samples
Typical samples for this measurement are:
-
Semi-crystalline polymers
-
Micelles
Have a look at the following application note that shows simultaneous SAXS/WAXS measurements of a semi-crystalline polymer during thermal processing which enable the determination of the route for phase transformation.
Methods & standards
No particular standards & methods are described in the literature.
XSACT analysis software is used first to display the structure evolution with temperature, and secondly for quantitative study.
Why use SAXS for in situ studies?
Advantages of SAXS for dynamic studies:
-
With SAXS, you can probe the changes in nanostructure as a function of temperature.
-
With simultaneous SAXS and WAXS, you can access atomic and mesoscale information at the same time, with no bias from reproducibility issues.
-
Simultaneous SAXS and WAXS data collection offers access to information over a broad range of length scales.
Products
All these measurements are possible directly in your lab.
Xeuss Pro
The Ultimate Solution for Nanoscale Characterization using SAXS/WAXS/GISAXS/USAXS/Imaging



































