Fast thermal studies of cocoa butter
Cocoa butter is a highly polymorphic compound exhibiting up to six crystalline forms of glycerides (fatty acids), each defined by different stability and melting point. In order to...
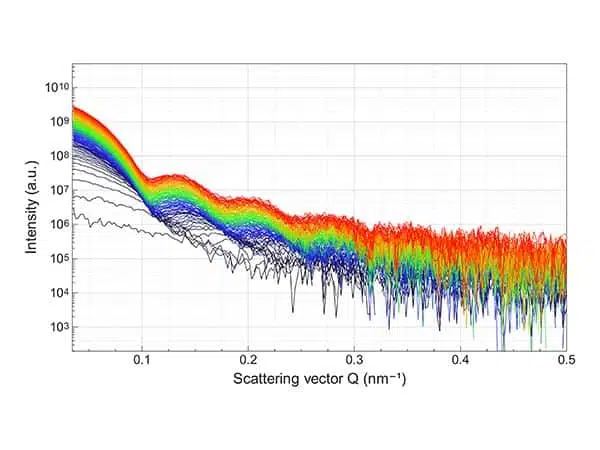
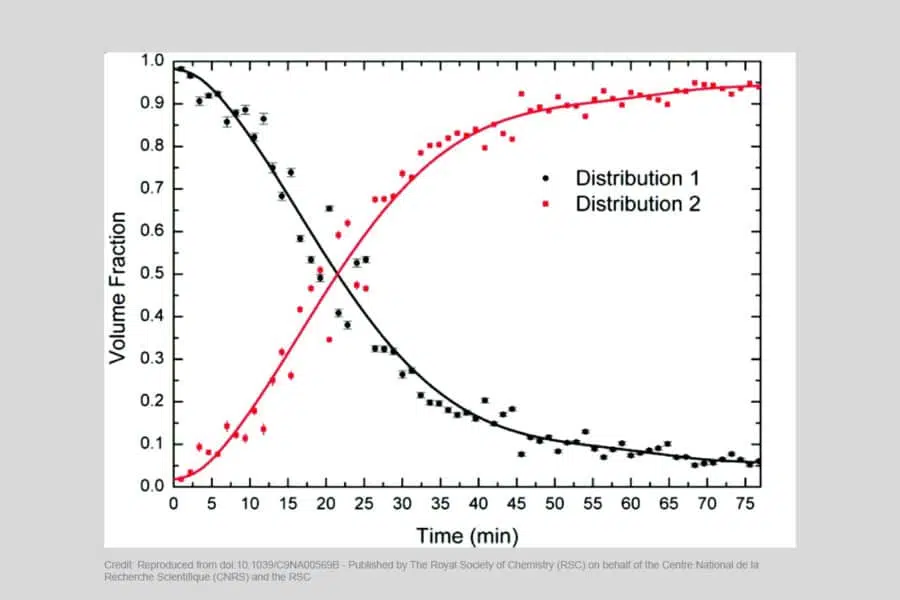
Batch data analysis of particle size temporal evolution studied with SAXS
Time-resolved Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) mesurements, performed during synthesis procedures or other chemical or physical reactions, have the potential to reveal valuable information which can...
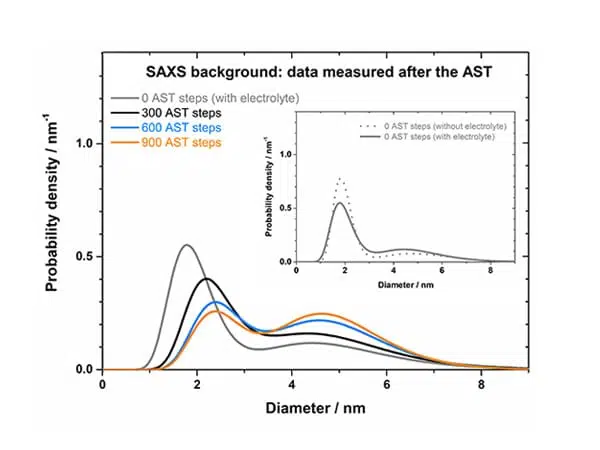
Can time-resolved degradation of catalysts be studied with operando laboratory SAXS?
To combat climate change, the use of renewable energies is regarded as one of the top priority actions to be implemented both by industries as well as private individuals. Today the use of so-called clean energy is ...
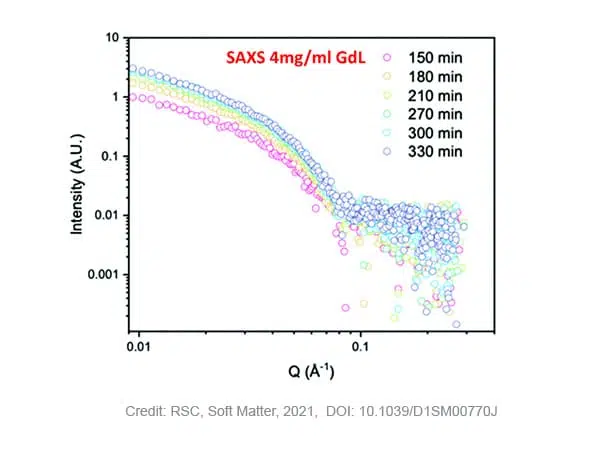
Understanding hydrogel phase transitions with SWAXS
Gels are interesting materials from many perspectives. Their ability to absorb large amounts of solvent results in a range of attractive material behaviors...
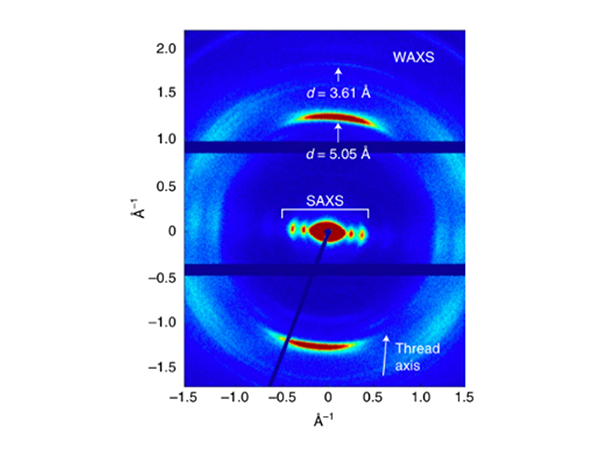
Self-assembly – How SAXS/WAXS helps investigate nanoribbons formed with aramid amphiphiles for more stability
Hierarchical self-assembly of small molecules is a tried and tested method to obtain nanostructured materials. The intrinsic dynamics and (bio)degradability of these materials ...
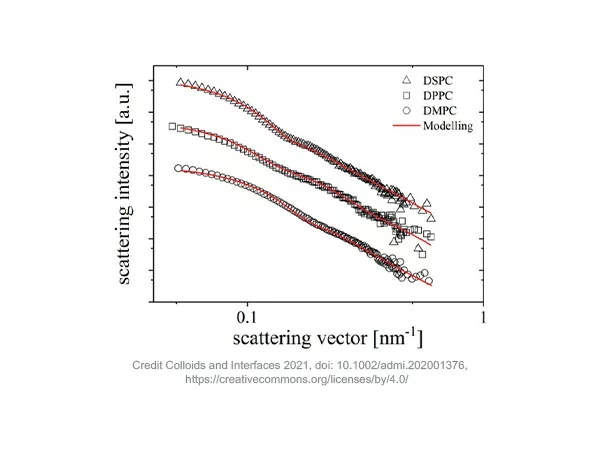
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering for the characterization of liposomes in pharmaceutical applications
- Application highlight - Small-Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) is an invaluable tool for the analysis of liposomes. Liposomes are a class of nanoparticles which are characterized by ...
New General Manager at Xenocs China
We are pleased to announce the arrival of Tao Lu as Xenocs China new General Manager and legal representative.
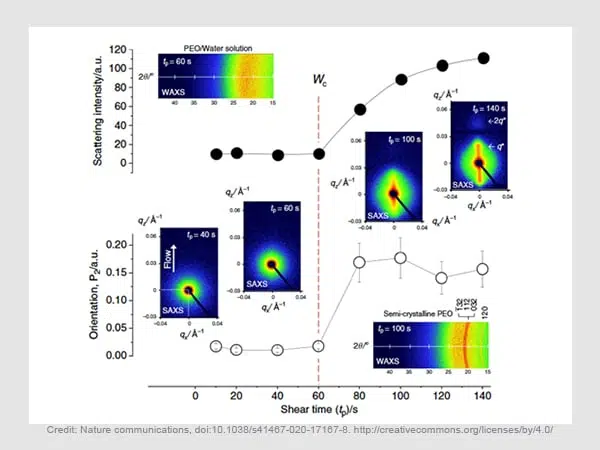
Mimicking nature: a shear-induced phase transition in poly(ethylene oxide)
Spider silk has been a thankful subject for biomimetic research over the course of many years. It is well-known for its incredible tensile strength and biocompatibility...
In-situ Small Angle X-ray Scattering for nanoparticle characterization
- Application highlight - Nanoparticles are characterized by the fact that they have at least one dimension in the nanometer range, i.e. between 1 and 100 nanometers. This means that ...